Hi Patrick
This was a difficult question on monetary transmission mechanisms.
You need to think about
how an increase in the money supply increases real output, ie the links in the chain; and then consider what determines the
strengths of these links.
The mechanism is as follows:
1. An increase in the money supply decreases interest rates.
2. A decrease in interest rates increases investment (and consumption and possibly net exports) and aggregate demand and therefore real output (as long as there is excess capacity).
The greater the strengths of these links, the greater the impact of an increase in the money supply on real output. So let’s examine these links more closely.
If the central bank increases the money supply by buying bonds in the open market, this increases the price of bonds and hence decreases the return on the bonds (ie decreases the rate of interest). This will encourage people to sell their bonds and hold cash instead. How far interest rates have to fall to achieve this depends on the elasticity of demand for money with respect to interest rates. The
more interest-inelastic the demand for money (ie the steeper the demand for money curve) the greater the drop in interest rates required to encourage people to part with their bonds and hold more money and hence restore money market equilibrium, as illustrated in the diagram below.
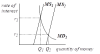
How much investment increases in response to the fall in interest rates depends on the elasticity of demand for investment with respect to interest rates. The more
interest-elastic the demand for investment, the greater the increase in investment in response to the fall in interest rates.
So the correct answer is Option D.
I hope that helps?