A
Adithyan
Member
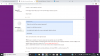
W(0)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">W(0)W(0) is just a constant so it has zero variance and an expected value of, well, W(0)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">W(0)W(0).
σB(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">σB(t)σB(t) is a constant multiple of standard Brownian motion (which we know has a N(0,t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">N(0,t)N(0,t) distribution. Therefore σB(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">σB(t)σB(t) has an expected value of zero and a variance of σ2t" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">σ2tσ2t (are you happy about this bit?).
μ(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">μ(t)μ(t) is a deterministic function in t" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">tt so it has zero variance and an expected value of μ(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">μ(t)μ(t).
This means that log⁡S(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">logS(t)logS(t) must be normally distributed, with mean W(0)+μ(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">W(0)+μ(t)W(0)+μ(t) and variance σ2t" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">σ2tσ2t.
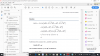
σB(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">σB(t)σB(t) is a constant multiple of standard Brownian motion (which we know has a N(0,t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">N(0,t)N(0,t) distribution. Therefore σB(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">σB(t)σB(t) has an expected value of zero and a variance of σ2t" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">σ2tσ2t (are you happy about this bit?).
μ(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">μ(t)μ(t) is a deterministic function in t" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">tt so it has zero variance and an expected value of μ(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">μ(t)μ(t).
This means that log⁡S(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">logS(t)logS(t) must be normally distributed, with mean W(0)+μ(t)" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">W(0)+μ(t)W(0)+μ(t) and variance σ2t" role="presentation" style="display: inline; line-height: normal; overflow-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; position: relative;">σ2tσ2t.